Piping Plant Design Calculations with Fabrication Detailing: A Complete Guide
Piping Plant Design is a crucial engineering discipline that integrates complex systems of pipelines in industrial facilities to ensure smooth fluid and gas transport. Whether it’s oil & gas, petrochemicals, power plants, or water treatment facilities, a well-executed piping design ensures optimal performance, safety, and compliance with international standards.
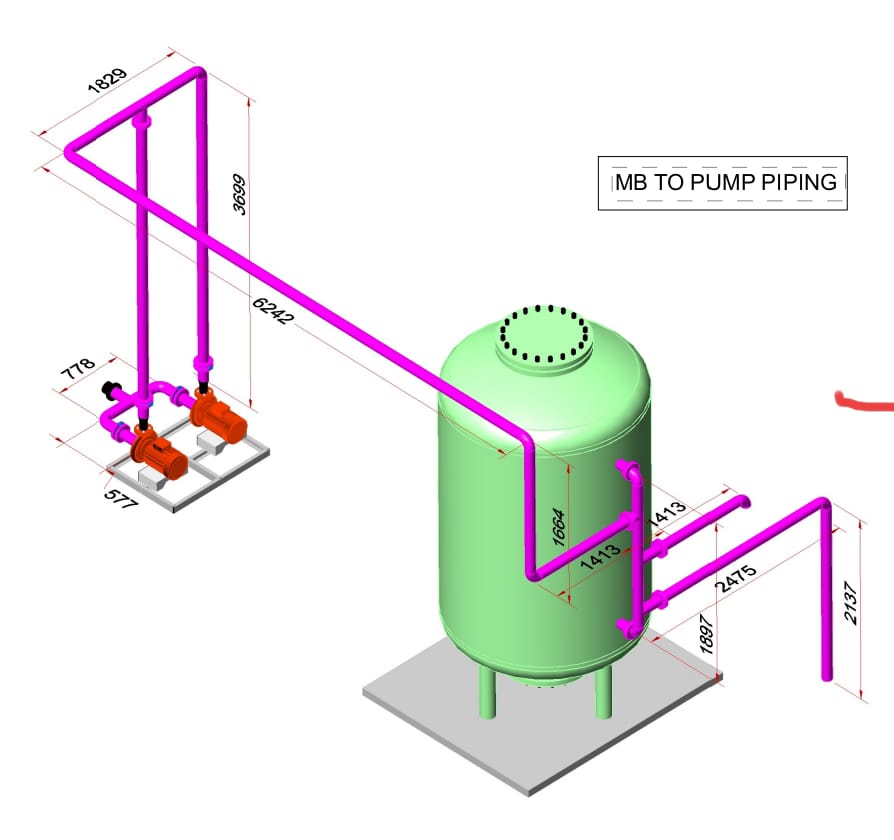
This article explores the critical components of Piping Plant Design, covering essential calculations, fabrication detailing, and the role of engineering documents like Pipe Isometrics, General Arrangement Drawings (GADs), Process Flow Diagrams (PFDs), Piping & Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs), and Layout Detailing. We’ll also explain the importance of a Material Take-Off (MTO) in successful project execution.
Importance of Piping Plant Design
The foundation of any process plant lies in its piping network. It connects various equipment such as pumps, compressors, heat exchangers, and reactors, enabling efficient process flow. A robust Piping Plant Design ensures:
Compliance with safety standards (ASME, ANSI, ISO)
Efficient layout and space management
Cost optimization through accurate material estimation
Seamless fabrication and installation
Core Design Calculations in Piping Plant Design
Design calculations form the backbone of any piping project. These calculations determine the pipe size, wall thickness, pressure ratings, flow velocity, and stress analysis. Key parameters include:
1. Pipe Sizing and Flow Calculations
Proper pipe sizing ensures fluid velocity stays within acceptable limits to minimize pressure loss and erosion. Calculations are based on:
- Bernoulli’s principle
- Darcy-Weisbach equation
- Flow rate (Q), velocity (v), and diameter (D)
2. Pressure Drop Analysis
Accurate pressure drop calculation helps in designing pumps and compressors. This includes friction losses, fittings, valves, and elevation changes.
3. Stress and Flexibility Analysis
Piping systems experience thermal expansion, weight loads, and internal pressure. Tools like CAESAR II are used to evaluate:
- Expansion loops
- Anchors and supports
- Stress at bends and tees
4. Wall Thickness Calculation
Using ASME B31.3 or B31.1 codes, wall thickness is determined based on pressure, temperature, material strength, and corrosion allowance.
Fabrication Detailing in Piping Projects
Fabrication detailing translates engineering design into buildable formats. It includes the creation of precise drawings and documentation for shop fabrication and field installation.
1. Pipe Isometrics
Pipe isometric drawings are 2D representations of 3D piping systems. They display:
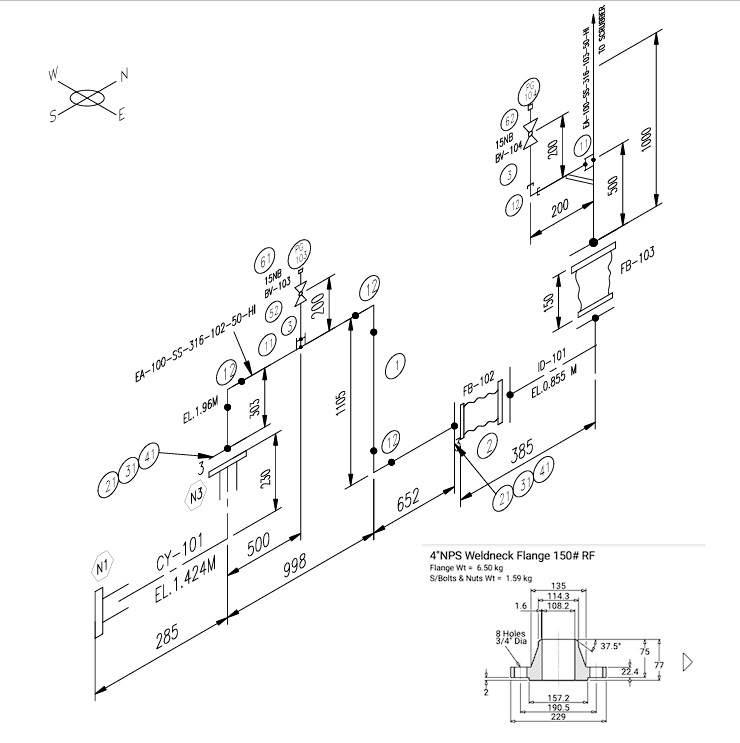
- Line number
- Dimensions and angles
- Weld points
- Support locations
- Bill of materials (BOM)
Isos are critical for spool fabrication and accurate welding in the shop or on-site.
2. General Arrangement Drawings (GADs)
GADs provide a top, front, and side view of the piping layout within a facility. They show equipment locations, pipe routing, platforms, and access ways.
3. Piping & Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs)
P&IDs are schematic representations showing:
- Process equipment
- Control valves and instruments
- Line tags and service codes
- Safety devices and interlocks
They serve as the master reference for process and instrumentation control.
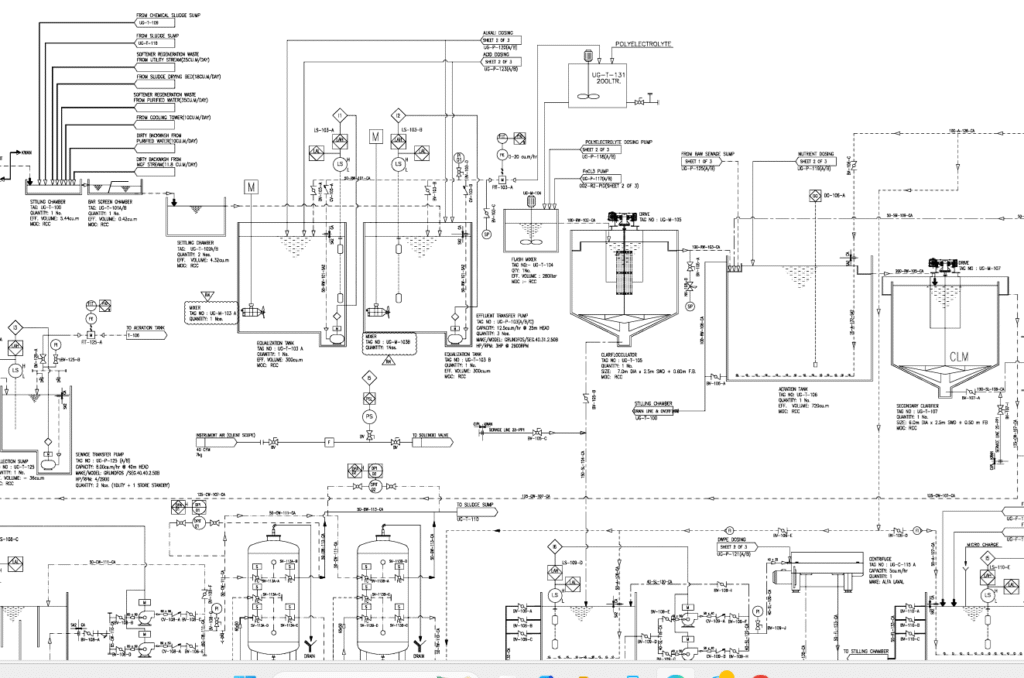
4. Process Flow Diagrams (PFDs)
PFDs illustrate the overall flow of materials and energy through a plant. These diagrams are used in early design stages and focus on:
- Mass balance
- Major equipment
- Basic control loops
Layout Detailing in Piping Design
Layout detailing ensures all plant components are installed in a logical, accessible, and safe manner. The layout must consider:
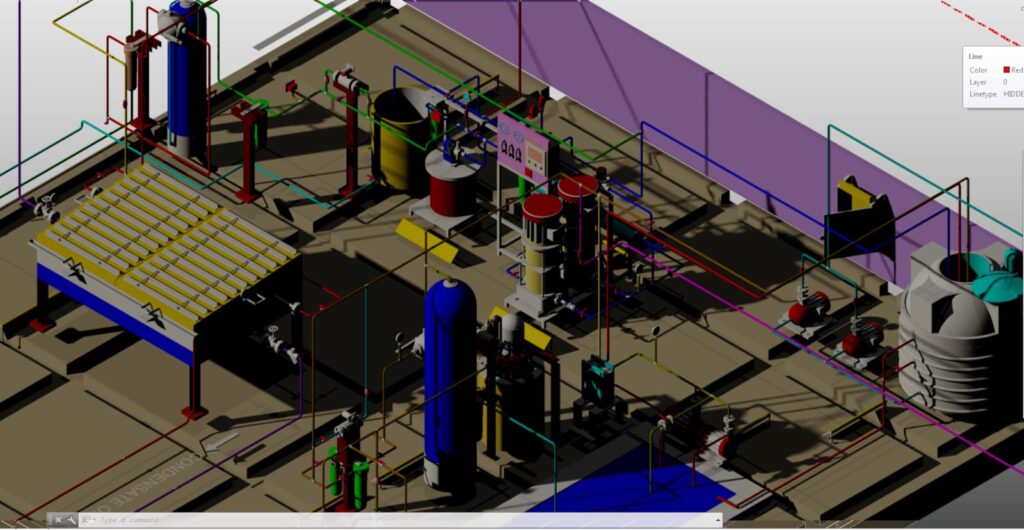
- Maintenance space
- Pipe supports and stress-relief locations
- Thermal expansion paths
- Accessibility to instruments and valves
Material Take-Off (MTO): Planning and Cost Control
MTO is a comprehensive list of all materials required for a project. It is generated from isometrics, GADs, and P&IDs. MTO helps in:
- Procurement planning
- Budget estimation
- Inventory control
- Reducing material wastage
A well-prepared MTO ensures timely project execution without delays due to material shortages.
Benefits of Integrated Piping Plant Design and Fabrication Detailing
✅ Enhanced Accuracy
Accurate calculations and detailed drawings reduce field errors and rework.
✅ Improved Project Coordination
Integrated design and detailing improve coordination among design, procurement, and construction teams.
✅ Reduced Costs
Efficient layout and accurate MTO help reduce material and labor costs.
✅ Faster Project Execution
With clear fabrication drawings and streamlined procurement, project timelines are shortened significantly.
Conclusion
Piping Plant Design is a complex but essential aspect of industrial project development. From design calculations to fabrication detailing, every step must be handled with precision and expertise. Leveraging advanced software tools and industry standards, engineers can develop efficient, safe, and cost-effective piping systems.
Our Social Presence: LinkedIn
For successful project execution, integrating pipe isometrics, GADs, PFDs, P&IDs, layout detailing, and an accurate Material Take-Off is critical. Investing in skilled piping design ensures not just compliance, but operational excellence and long-term reliability.
Need help with your Piping Plant Design project?
Our expert engineers can deliver optimized designs with complete fabrication detailing to meet your plant’s operational and safety goals. Contact us today for a consultation!
GET IN TOUCH

![3D Cutting Edge Piping Plant Design 1 piping isometric drawings are the backbone of successful execution. These detailed, three-dimensional representations of piping systems are essential for fabrication, installation, and maintenance. At [Your Company Name], we specialize in delivering high-quality piping isometric drawings that streamline your project from concept to completion.](https://coredesigncenter.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/3D-PROCESS-PLANT-DESIGN-1.png)