Invest in Expert Heat Exchanger Design
In the realm of industrial thermal management, Heat Exchanger Design plays a pivotal role in ensuring energy efficiency, process reliability, and operational safety. Among the various types of heat exchangers, the shell and tube configuration stand out as the most versatile and widely adopted solution across industries such as petrochemical, power generation, HVAC, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
This article delves into the intricacies of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design, highlighting key engineering principles, fabrication detailing, and performance optimization strategies that define a high-quality thermal exchange system.
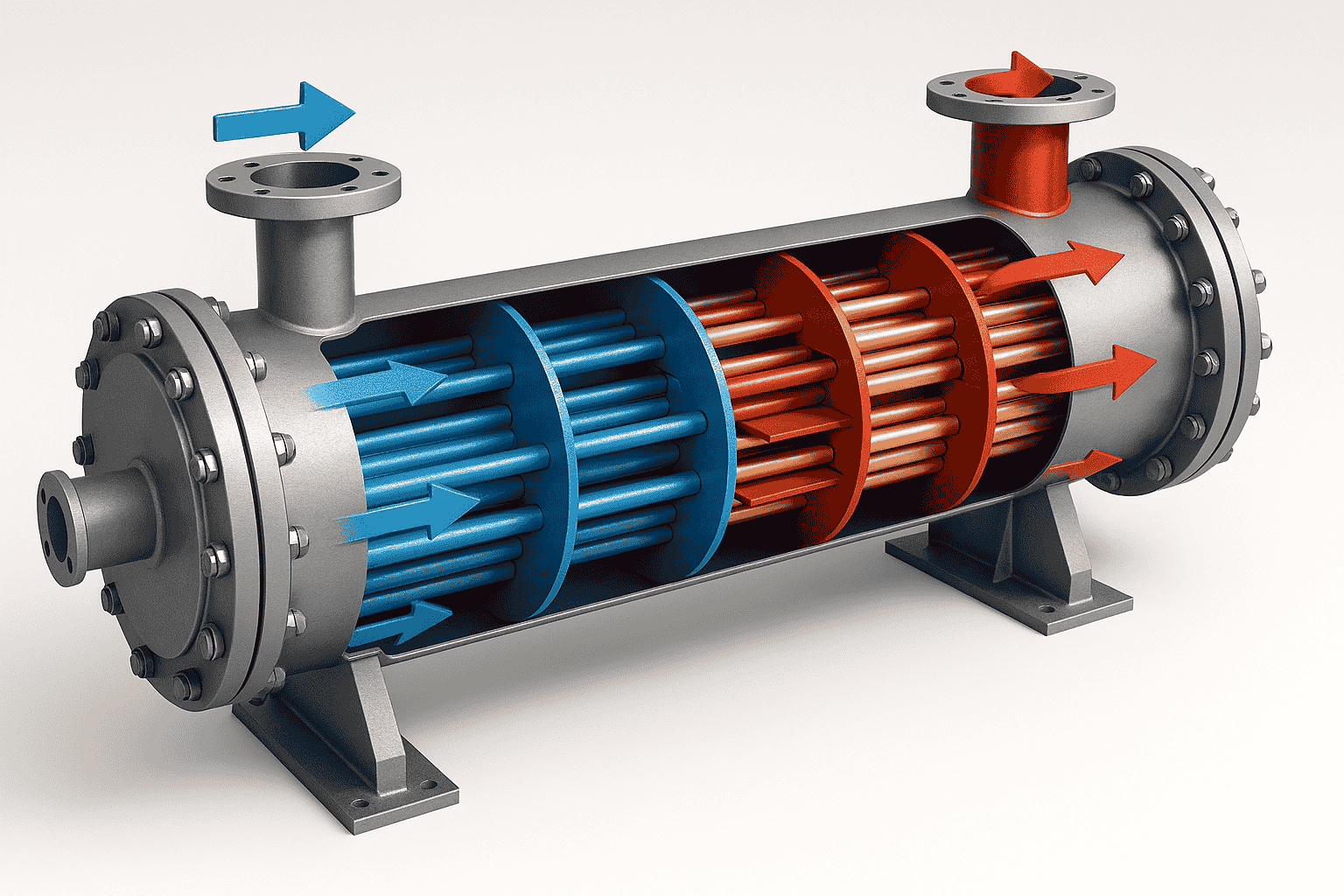
What Is a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger?
A shell and tube heat exchanger consists of a series of tubes enclosed within a cylindrical shell. One fluid flow through the tubes, while another fluid flows over the tubes within the shell, facilitating efficient thermal exchange. This design is favored for its robustness, scalability, and ability to handle high pressures and temperatures.
Key Components:
- Shell: The outer casing that holds the tube bundle.
- Tube Bundle: Comprising straight or U-shaped tubes, typically made of stainless steel, copper, or titanium.
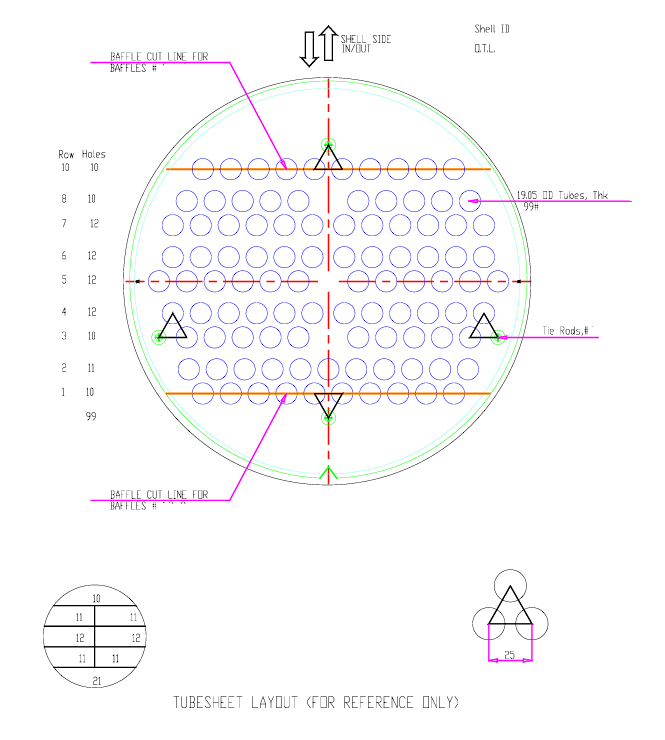
- Baffles: Plates that direct fluid flow within the shell to enhance turbulence and heat transfer.
- Tube Sheets: Metal plates that secure the tubes at both ends.
- Nozzles and Flanges: For fluid inlet and outlet connections.
Principles of Heat Exchanger Design
Effective Heat Exchanger Design requires a deep understanding of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and material science. The goal is to maximize heat transfer while minimizing pressure drop, fouling, and mechanical stress.
Design Considerations:
- Thermal Load Requirements: Determining the amount of heat to be transferred between fluids.
- Flow Configuration: Options include parallel flow, counterflow, and crossflow, each affecting efficiency.
- Tube Diameter and Length: Influences surface area and pressure drop.
- Material Selection: Based on corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength.
- Fouling Factors: Designing for easy cleaning and maintenance to prevent performance degradation.
Advanced simulation tools and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) are often employed to model fluid behavior and optimize the exchanger’s geometry for peak performance.
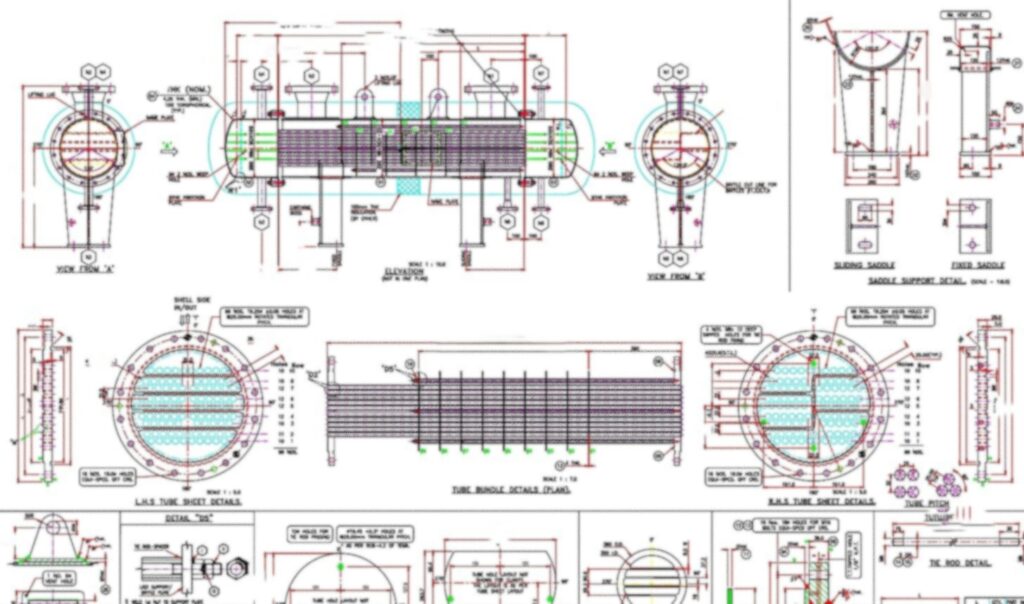
Fabrication Detailing: Precision Meets Durability
Fabrication is where design meets reality. Precision in manufacturing ensures that the Heat Exchanger Design translates into a reliable, long-lasting product.
Fabrication Steps:
- Material Procurement: High-grade metals are sourced based on design specs and operating conditions.
- Tube Sheet Drilling and Machining: CNC machines ensure accurate hole placement and alignment.
- Tube Insertion and Expansion: Tubes are inserted into the sheets and expanded to form a leak-proof seal.
- Welding and Assembly: Critical joints are welded using TIG or MIG techniques to ensure structural integrity.
- Baffle Installation: Strategically placed to optimize flow dynamics.
- Pressure Testing: Hydrostatic and pneumatic tests validate the exchanger’s ability to withstand operating pressures.
- Surface Treatment: Anti-corrosion coatings and polishing enhance durability and hygiene, especially in food-grade applications.
Quality control is paramount. Every unit undergoes rigorous inspection to meet ASME, TEMA, and ISO standards.
Performance Optimization
To ensure that your Heat Exchanger Design delivers optimal performance over its lifecycle, several strategies are employed:
- Enhanced Surface Tubes: Corrugated or finned tubes increase surface area and turbulence.
- Variable Baffle Spacing: Adjusting baffle spacing can reduce pressure drop and improve heat transfer.
- Modular Design: Facilitates scalability and easy maintenance.
- Smart Monitoring: Integration of sensors for real-time temperature and pressure tracking.
These enhancements not only boost efficiency but also reduce operational costs and downtime.
Applications Across Industries
Shell and tube heat exchangers are the backbone of thermal systems in:
| Industry | Application Example |
|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Crude oil preheating, gas cooling |
| Power Generation | Steam condensation, feedwater heating |
| Chemical | Reactor cooling, solvent recovery |
| HVAC | Chiller systems, heat recovery |
| Food & Beverage | Pasteurization, CIP systems |
Their adaptability to various fluids, pressures, and temperatures makes them indispensable in both batch and continuous processes.
Why Invest in Expert Heat Exchanger Design?
Choosing a partner with deep expertise in Heat Exchanger Design ensures:
- Custom Solutions tailored to your process requirements.
- Energy Efficiency through optimized thermal performance.
- Regulatory Compliance with global engineering standards.
- Long-Term Reliability backed by precision fabrication and quality materials.
- For Process plant Design: Check our process plant design
Whether you’re upgrading an existing system or building a new plant, investing in high-quality design and fabrication pays dividends in performance, safety, and sustainability.
Let’s Build Your Next Heat Exchanger
At Core Design Center, we specialize in end-to-end Heat Exchanger Design and fabrication services. From concept to commissioning, our team of engineers, fabricators, and quality experts work collaboratively to deliver solutions that exceed expectations.
Our Social Presence – LinkedIn
Ready to elevate your thermal systems? Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our shell and tube heat exchangers can transform your operations.
GET IN TOUCH FOR A