In the world of industrial engineering, process plant design is the backbone of safe, efficient, and cost-effective operations. Whether you’re working on a water treatment facility, a crude oil filtration unit, or a heavy fuel oil (HFO) processing plant, accurate design calculations are essential to ensure optimal performance and regulatory compliance.
This article explores the key principles, formulas, and standards used in process plant design, with a focus on piping systems, pressure drop analysis, tank sizing, and international codes like ASME, API, and ISO.
Understanding Process Plant Design
Process plant design refers to the planning and engineering of systems that convert raw materials into valuable products through chemical, physical, or mechanical processes. These plants include:
- Water Treatment Plants – for purification and recycling
- Crude Oil Filtration Units – for separating impurities before refining
- Distillation Columns – for producing LPG, petrol, diesel, and other fuels
- HFO Processing Plants – for handling viscous fuels in power generation
Each of these facilities requires precise calculations to ensure that piping, tanks, and equipment are sized correctly and operate safely under varying conditions.
Basic Design Calculations for Process Plants
A: Piping Design and Line Sizing
Proper pipe sizing is critical for maintaining flow rates, minimizing energy losses, and avoiding operational hazards. The following formulas are commonly used:
1: Pipe Flow Rate
To calculate the flow rate (Q) in a pipe:
Q = A*V
Where:
- Q = Flow rate (m³/s)
- A = Cross-sectional area of pipe (m²)
- V = Fluid velocity (m/s)
2: Pressure Drop Calculation
Pressure drop across a pipe is calculated using the Darcy-Weisbach equation:
🔺P = f \times \frac{L}{D} \times \frac{\rho V^2}{2}
Where:
- 🔺 P = Pressure drop (Pa)
- f = Friction factor
- L = Length of pipe (m)
- D = Diameter of pipe (m)
- \rho = Fluid density (kg/m³)
- V = Velocity (m/s)
These calculations help determine the optimal pipe diameter and material for transporting water, oil, or gas efficiently.
B: Tank Design Assumptions
Tanks are used for storage, mixing, and reaction processes. Their design depends on volume, pressure, temperature, and fluid properties.
1: Volume Calculation
For cylindrical tanks:
V = \pi \times r^2 \times h
Where:
- V = Volume (m³)
- r = Radius (m)
- h = Height (m)
2: Pressure Rating
Tank pressure ratings must comply with ASME Section VIII for pressure vessels. Design pressure is typically 10–25% above operating pressure to ensure safety.
Process Piping Codes and Standards
Compliance with international standards is non-negotiable in process plant design. These codes ensure safety, reliability, and interoperability across industries.
3: ASME Codes
- ASME B31.3 – Process Piping
- ASME Section VIII – Pressure Vessel Design
- ASME B16.5 – Flanges and Fittings
4: API Standards
- API 650 – Welded Tanks for Oil Storage
- API 610 – Centrifugal Pumps
- API 520/521 – Pressure Relief Systems
5: ISO Standards
- ISO 9001 – Quality Management
- ISO 14692 – GRP Piping Systems
- ISO 10628 – Diagrams for Chemical and Process Engineering
These standards guide everything from material selection to fabrication and inspection.
Real-World Examples of Process Plants-
A: Water Treatment Plant
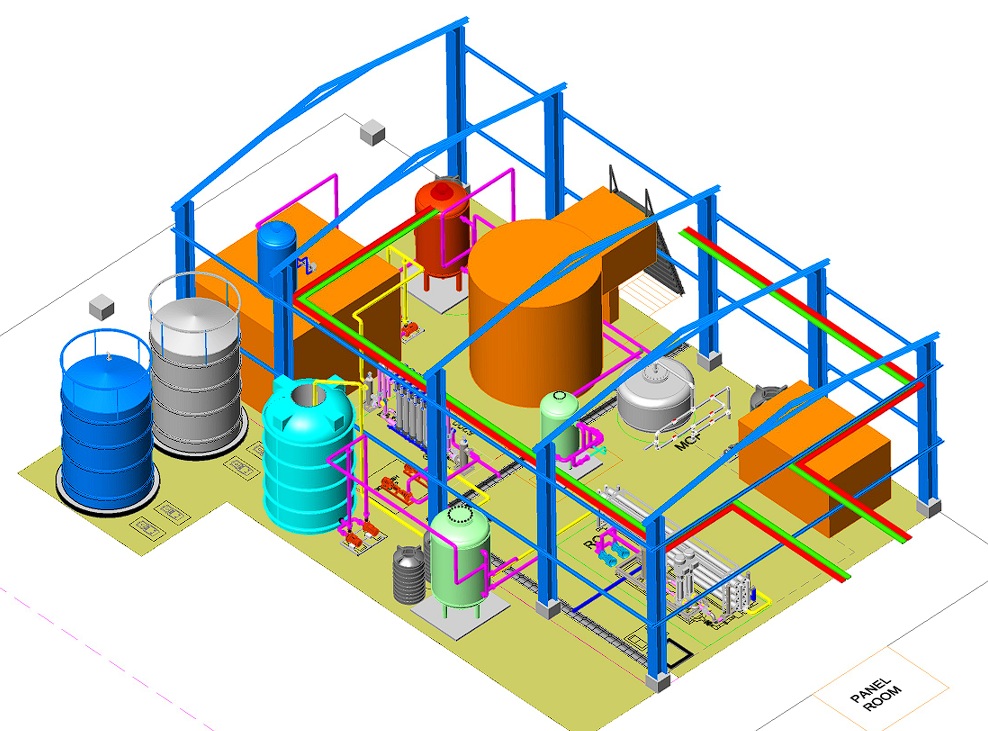
In a water solution plant, piping must be designed to handle varying flow rates and chemical concentrations. Pressure drop calculations ensure that pumps are sized correctly to maintain flow through filters and membranes.
B: Crude Oil Filtration Unit
These units remove particulates and water from crude oil before refining. Line sizing and tank design are crucial to handle high-viscosity fluids and maintain throughput.
C: Distillation Columns for Fuel Production
Distillation columns separate crude oil into LPG, petrol, diesel, and other products. The design involves:
- Thermal calculations for heat exchangers
- Pressure drop analysis in trays and packing
- Piping design for feed and product lines
Each product stream must be routed through properly sized pipes and stored in tanks designed to API and ASME standards.
Why Choose Core Design Center?
Precision-Driven Engineering
We don’t guess—we calculate. Every pressure drop, flow rate, and thermal gradient is backed by rigorous simulation and real-world validation. Our designs optimize efficiency, safety, and cost from the first draft to final execution.
End-to-End Process Insight
From crude oil distillation to multi-stream separation (LPG, petrol, diesel, kerosene), we understand the full lifecycle of process plants. Our models aren’t just theoretical—they’re built for execution, maintenance, and scale.
Modular, Scalable Solutions
Whether you’re designing a pilot plant or scaling to full industrial capacity, our workflows adapt. We build modular systems that grow with your business—without redesigning from scratch.
Academic Rigor Meets Industrial Reality
We bridge the gap between textbook theory and field execution. Our training programs and design reviews empower teams to understand not just what works, but why it works.
Customized Calculations
Every plant is unique. We tailor our calculations to your feedstock, climate, regulatory constraints, and operational goals. No templates—just intelligent design.
💡 Innovation with Irony
We turn complexity into clarity—and sometimes, into content. Our visual workflows and infographics make even the most technical designs understandable, teachable, and brandable.
Our Social Presence
Conclusion
Effective process plant design is a blend of engineering precision, regulatory compliance, and practical experience. From calculating pipe diameters to selecting the right tank materials, every decision impact safety, efficiency, and profitability.
Whether you’re designing a water treatment facility or a multi-product refinery, mastering these calculations and standards is key to delivering successful projects. For more insights or design support, feel free to reach out—we’re here to help you build smarter, safer, and more sustainable process plants.
GET IN TOUCH

![Cutting Edge 3D Process Plant Design Calculations 1 piping isometric drawings are the backbone of successful execution. These detailed, three-dimensional representations of piping systems are essential for fabrication, installation, and maintenance. At [Your Company Name], we specialize in delivering high-quality piping isometric drawings that streamline your project from concept to completion.](https://coredesigncenter.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/3D-PROCESS-PLANT-DESIGN-1.png)